Yang-Jun Wen, Ya-Wen Zhang, Jin Zhang, Jian-Ying Feng, Jim M. Dunwell, Yuan-Ming Zhang*. An efficient multi-locus mixed model framework for the detection of small and linked QTLs in F2.
Briefings in Bioinformatics, online,18 July 2018, DOI: 10.1093/bib/bby058. (5 years IF:7.065)
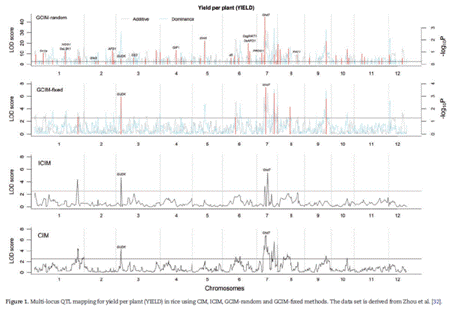
In the genetic system that regulates complex traits, metabolites, gene expression levels, RNA editing levels and DNA methylation, a series of small and linked genes exist. To date, however, little is known about how to design an efficient framework for the detection of these kinds of genes. In this article, we propose a genome-wide composite interval mapping (GCIM) in F2. First, controlling polygenic background via selecting markers in the genome scanning of linkage analysis was replaced by estimating polygenic variance in a genome-wide association study. This can control large, middle and minor polygenic backgrounds in genome scanning. Then, additive and dominant effects for each putative quantitative trait locus (QTL) were separately scanned so that a negative logarithm P-value curve against genome position could be separately obtained for each kind of effect.